OSHA Z-Tables Explained: Understanding Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs)
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Z-Tables are workplace safety standards that establish Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) for hazardous substances in occupational settings. These tables are found in 29 CFR 1910.1000 and help protect workers from harmful exposure to airborne contaminants, such as gases, vapors, dust, and fumes.
1. What are OSHA Z-Tables?
OSHA’s Z-Tables define the maximum allowable concentrations of specific chemicals and substances that workers can be exposed to over a set period. These exposure limits are measured in:
- PPM (Parts Per Million) – Used for gases and vapors.
- MG/M³ (Milligrams per Cubic Meter) – Used for particulates, dust, or fumes.
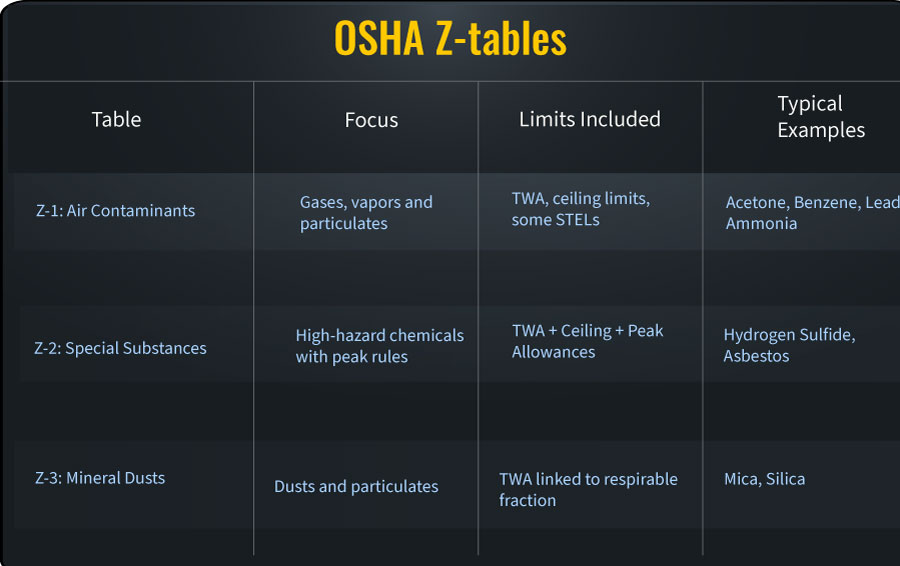
There are three main Z-Tables that cover different types of airborne contaminants:
| Z-Table | Covers |
|---|---|
| Table Z-1 | Air contaminants (gases, vapors, fumes, and particulates) |
| Table Z-2 | Substances with specific short-term and ceiling limits |
| Table Z-3 | Mineral dust exposure limits (e.g., silica, coal dust) |
2. Breakdown of OSHA Z-Tables
A. Table Z-1: Limits for Air Contaminants
This table sets Time-Weighted Average (TWA) exposure limits, meaning the average exposure a worker can have over an 8-hour work shift.
- It applies to toxic gases, vapors, mists, and fumes commonly found in industrial settings.
- Some substances have a Ceiling Limit (C), which means exposure must never exceed that level.
Example Substances in Table Z-1:
| Substance | CAS Number | TWA (8-hour limit) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | 630-08-0 | 50 ppm |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 7664-41-7 | 50 ppm |
| Benzene | 71-43-2 | 1 ppm |
| Lead (as Pb fumes and dust) | 7439-92-1 | 0.05 mg/m³ |
Key Notes:
- TWA means that exposure over 8 hours cannot exceed the listed value.
- Some chemicals, like Benzene, have both a PEL and an action level, meaning extra precautions must be taken at lower exposures.
B. Table Z-2: Limits for Substances with Peak and Ceiling Limits
This table includes chemicals with short-term exposure limits (STELs) and ceiling concentrations, which means:
- Short-Term Exposure Limit (STEL): The max concentration allowed for 15 minutes of exposure.
- Ceiling (C): The level that must never be exceeded, even briefly.
Example Substances in Table Z-2:
| Substance | TWA (8-hour limit) | STEL (15-min limit) | Ceiling (C) Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) | 20 ppm | 50 ppm (peak) | 20 ppm (max) |
| Toluene | 200 ppm | 300 ppm (ceiling) | – |
| Formaldehyde | 0.75 ppm | 2 ppm | – |
Key Notes:
- Exposures above the ceiling limit are not allowed at any time.
- STELs allow higher concentrations but only for short durations.
C. Table Z-3: Limits for Mineral Dust
Table Z-3 covers dusts and mineral particulates, such as:
- Silica
- Coal dust
- Portland cement dust
Example Substances in Table Z-3:
| Substance | TWA Limit |
|---|---|
| Silica, Crystalline (Quartz, respirable fraction) | 10 mg/m³ ÷ (%SiO₂ + 2) |
| Coal Dust (Respirable fraction) | 2.4 mg/m³ |
| Portland Cement Dust | 15 mg/m³ |
Key Notes:
- Exposure limits vary based on respirable vs. total dust.
- Crystalline silica has a formula-based limit to adjust for variable toxicity.
3. How to Use OSHA Z-Tables in the Workplace
Employers must:
- Monitor Air Quality: Use industrial hygiene sampling to check exposure levels.
- Apply Engineering Controls: Use ventilation, enclosed systems, or process modifications to reduce airborne hazards.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) & Respirators: If exposure exceeds PELs, provide respiratory protection and proper PPE.
- Train Workers: Ensure employees understand exposure risks and safety protocols.
- Follow OSHA Recordkeeping Rules: Maintain air monitoring records and exposure logs.
4. Regulatory Compliance and OSHA Enforcement
OSHA enforces Z-Table limits through:
- Workplace Inspections
- Employer Reporting Requirements
- Fines and Citations for non-compliance
Failure to comply can lead to serious penalties, especially for highly hazardous substances like Benzene, Lead, and Silica.
5. Key Takeaways
✅ OSHA’s Z-Tables set legal exposure limits for hazardous workplace substances.
✅ Table Z-1 covers general air contaminants (TWA limits).
✅ Table Z-2 sets short-term and ceiling limits for highly toxic substances.
✅ Table Z-3 regulates dust and mineral particulates (e.g., silica, coal dust).
✅ Employers must monitor air quality, control exposure, and protect workers.

